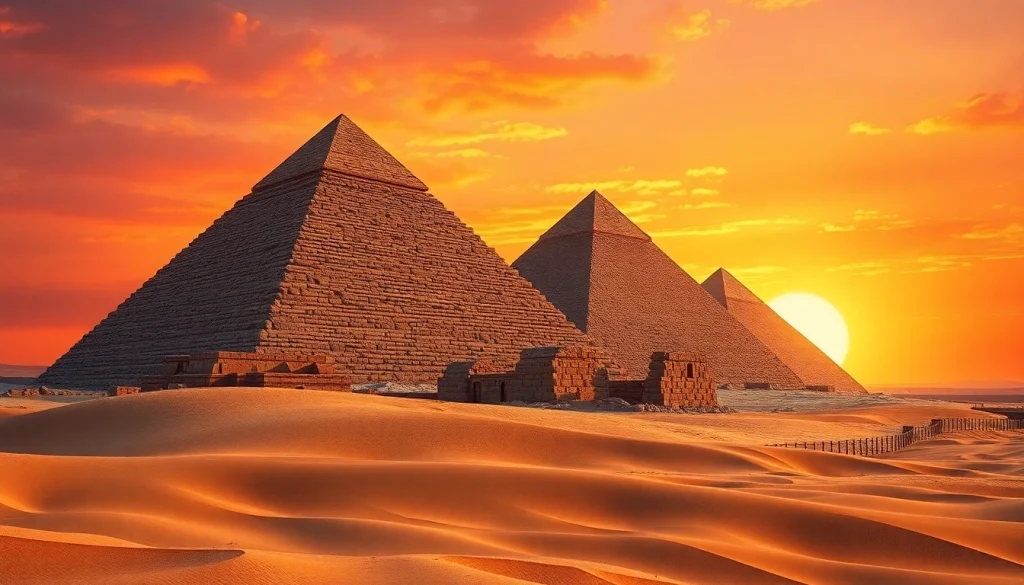
Understanding the Origins of Piraminds
The Historical Context of Piraminds
Piraminds have long intrigued historians and archaeologists alike. These monumental structures primarily originated in ancient Egypt, around 2700 BCE, during the third dynastic period. Initially built as tombs for pharaohs, piraminds exemplify the civilization’s advancements in architecture and construction. The most notable among them, the Great Pyramid of Giza, served not only as a burial place but also as a testament to the pharaoh’s divine power and connection to the gods. The vast cultural and spiritual beliefs of ancient Egyptians heavily influenced the design and purpose of these structures.
Architectural Features of Piraminds
Architecturally, piraminds feature distinctive triangular shapes that symbolize the ascent to the heavens. The pyramidal structure allows for a strong foundation that can support significant weight. Notably, the use of polished limestone casing stones, which originally covered the structures, added to their grandeur by reflecting sunlight. Inside, a labyrinth of chambers and passageways reflects advanced engineering techniques, where the main burial chamber typically houses the sarcophagus of the pharaoh as well as numerous artifacts intended for the afterlife.
Cultural Significance of Piraminds in Ancient Egypt
The significance of piraminds transcends mere architectural achievement. They are deeply rooted in ancient Egyptian belief systems, particularly regarding the afterlife. The construction of these structures was seen as a way for the deceased pharaoh to traverse into immortality. Rituals and ceremonies often took place in their vicinity, strengthening their ties to religion and daily life. The layout of piraminds was intentionally designed to align with celestial bodies, thus reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ understanding of astronomy.
Exploring the Construction Techniques of Piraminds
Material Choices for Building Piraminds
The construction of piraminds relied heavily on locally available materials. Limestone was primarily used due to its durability and ease of transportation from nearby quarries. Granite, used in the innermost chambers, offered exceptional strength and was often transported from Aswan, located more than 800 kilometers away. Together, these materials not only provided structural integrity but also reflected ancient Egyptian aesthetics and symbolism.
Labor Force: Who Built the Piraminds?
The labor force responsible for building piraminds remains a subject of significant debate. Contrary to popular belief, the pyramids were not built by slaves; rather, they were constructed by skilled laborers who worked on the site on a rotating basis. This workforce included craftsmen, architects, and farmers—particularly during the inundation season when agricultural activities were minimal. Revealed records have indicated that these workers were organized into teams and were well-fed, receiving fair compensation for their labor.
Technological Innovations in Piramid Construction
Piramids showcase remarkable technological ingenuity. The ancient Egyptians utilized simple tools, including wooden sledges, levers, and ramps, to maneuver and lift massive stone blocks. The creation of the straight and stepped pyramid designs marked significant advancements in engineering. In addition, advancements in mathematics aided in achieving precise measurements and angles, essential for the stability and aesthetic appeal of the structures.
Modern Day Discoveries Related to Piraminds
Recent Archaeological Findings
Recent archaeological endeavors have unveiled exciting discoveries related to piraminds. Notably, scientists have detected hidden voids and chambers within the Great Pyramid, potentially reshaping historical understandings of its construction. These discoveries contribute to ongoing research regarding how ancient Egyptians managed the vast logistics of pyramid construction and burial practices.
Technological Advances in Studying Piraminds
Modern technology plays a pivotal role in the study of piraminds. Techniques such as infrared thermography and cosmic-ray muon radiography allow researchers to peer into the structures without disturbing them physically. These non-invasive methods have provided data regarding internal structures, leading to the identification of previously unknown chambers and passageways.
The Impact of Climate on Piraminds Preservation
Climate change poses significant challenges to the preservation of piraminds. Factors such as rising temperatures, increased humidity, and pollution greatly threaten their structural integrity. Preservation efforts must address these environmental stresses. Experts advocate for sustainable tourism and active restoration strategies to ensure these historical landmarks endure for future generations.
Piraminds as Tourist Destinations
Visitor Experiences at Piramid Sites
Piraminds serve as prominent tourist attractions, drawing millions annually to explore their grandeur. Visitor experiences range from guided tours that delve into the history and construction of these marvels to immersive cultural experiences that highlight ancient Egyptian customs. Essentially, they allow visitors to step into the past and witness sites that have withstood millennia.
Preservation Efforts for Piraminds
Efforts to preserve piraminds are crucial to maintain their integrity amid tourism challenges. Local governments and international organizations are collaborating on conservation initiatives, applying advanced techniques for restoration and damage assessment. Regular monitoring and public awareness campaigns are essential to educate tourists on the significance of responsible visitation.
Economic Impacts of Piramid Tourism
The economic implications of piramid tourism are substantial. They contribute to local economies, creating jobs and boosting related industries such as hospitality and transportation. However, this influx of visitors can also exert pressure on the surrounding environment. Striking a balance between promoting tourism and ensuring preservation is vital for sustainable economic growth.
FAQs about Piraminds
What are piraminds made of?
Piraminds are primarily constructed from limestone and granite, showcasing advanced ancient engineering.
How were piraminds built?
Piraminds were built using large stone blocks transported from quarries using manpower, sledges, and lubrication.
What purpose did piraminds serve?
Piraminds primarily served as monumental tombs for pharaohs, reflecting their divine status and journey into the afterlife.
Why are piraminds considered architectural marvels?
Piraminds are recognized for their precise alignments, massive scale, and complex interior structures, showcasing ancient engineering prowess.
Are there other types of piraminds?
Yes, aside from the famous Egyptian pyramids, there are Nubian and Mesoamerican piraminds, each with unique features and histories.
To explore more about piraminds, visit piraminds.