Getting Started with Gardening Basics
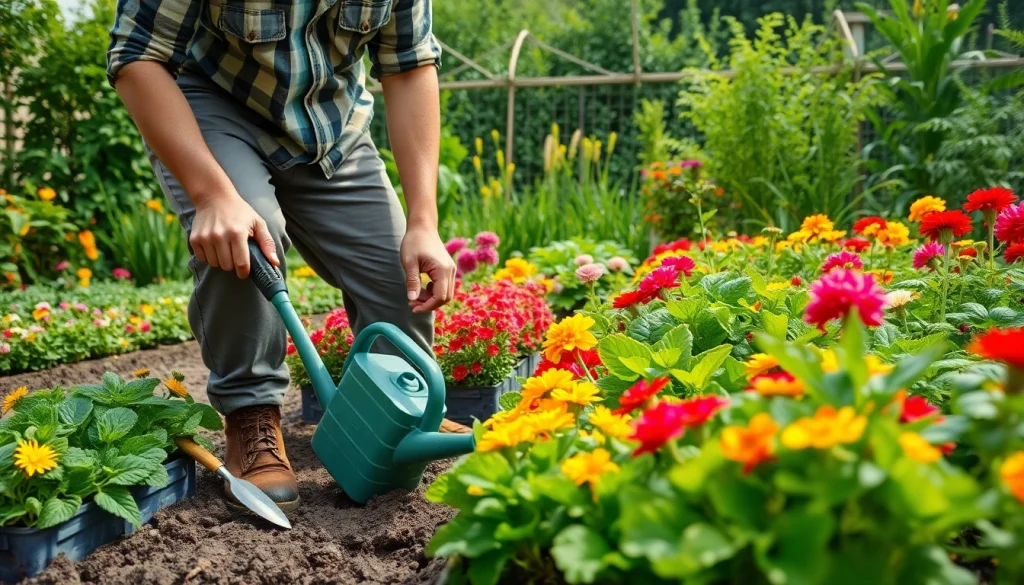
Gardening is more than just a hobby; it’s a way to connect with nature, relax your mind, and cultivate your own food or flowers. For beginners looking to dive into the world of plants, understanding the fundamentals of gardening is essential. Whether you dream of a vibrant flower garden or a productive vegetable patch, learning the basics lays the groundwork for success. To start your journey, visit Gardening websites or resources that provide extensive knowledge about the subject.
Understanding Soil Types and Preparation
Soil is the foundation of any garden, and understanding its types can significantly affect plant growth. There are three primary soil types: sandy, clay, and loamy. Sandy soil drains quickly but lacks nutrients, while clay soil holds water and nutrients but can become compacted. Loamy soil is a blend of both, offering the best of both worlds.
Before planting, preparing the soil is vital. This includes:
- Testing the Soil pH: Most plants prefer a pH of 6.0 to 7.0. Test kits are readily available at gardening centers.
- Amending the Soil: To improve earth quality, add organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure.
- Tilling: Aerate the soil by turning it over to ensure weed control and improve drainage.
Choosing the Right Plants for Your Space
Selecting the right plants is crucial for a thriving garden. Consider the following factors:
- Climate Zone: Different plants thrive in various climatic conditions. Familiarize yourself with hardiness zones to choose appropriate varieties.
- Sunlight Requirements: Understand the sunlight your garden receives daily to choose plants accordingly. Some plants prosper in full sun, while others prefer shade.
- Purpose: Decide if you want to grow flowers, vegetables, or herbs. Each has different care requirements and benefits.
Essential Gardening Tools Every Gardener Needs
Equipping yourself with the right tools will vastly improve your gardening experience. Essential tools include:
- Hand Trowel: Perfect for digging and planting small areas.
- Pruners: Necessary for trimming and maintaining plant health.
- Gardening Gloves: Protect your hands from thorns and soil.
- Watering Can or Hose: For efficient watering practices.
- Rake and Hoe: Useful for clearing debris and cultivating soil.
Planning Your Garden Layout
A well-designed garden layout maximizes space and ensures optimal plant growth. Consider the following elements when designing your garden:
Design Principles for a Successful Garden
Understanding basic design principles is crucial for creating a visually appealing and functional garden:
- Balance: Create symmetry or asymmetry in plant arrangements to draw the eye.
- Contrast: Use varying colors and textures to make certain plants stand out.
- Rhythm: Repeat plant varieties to establish a sense of harmony throughout the garden.
Companion Planting for Healthier Growth
Companion planting is an age-old practice where certain plants are grown together for mutual benefits. For example, tomatoes and basil thrive together, enhancing each other’s growth and flavor while deterring pests.
Key benefits include:
- Natural pest deterrence
- Improved nutrient uptake
- Enhanced growth rates
Seasonal Planting Guide
Understanding when to plant specific crops is vital. Each vegetable or flower has its own ideal planting times:
- Spring: Cool-season crops like peas, lettuce, and radishes are ideal for early planting.
- Summer: Warm-season crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers thrive in the summer heat.
- Fall: Late-season crops can include kale, garlic, and certain herbs that benefit from cooler temperatures.
Watering Techniques for Optimal Growth
Watering is one of the most critical aspects of gardening. Different plants have varying water needs, and knowing how to meet these needs is essential for robust growth.
Understanding Water Needs of Different Plants
Not all plants require the same amount of water. For instance:
- Succulents and cacti need minimal watering.
- Vegetables tend to need consistent moisture, while certain flowers may thrive with less.
- Always consider the local climate as it can affect the water requirements.
Watering Systems: Hand Watering vs. Irrigation
Choosing between hand watering and an irrigation system will depend on your garden’s size and layout:
- Hand Watering: Ideal for small gardens. Allows you to assess water needs closely.
- Irrigation Systems: Efficient for larger areas. Options include drip irrigation for targeted watering or soaker hoses for even coverage.
Strategies for Efficient Water Use
Implementing water-saving practices can enhance garden sustainability:
- Mulching: Helps retain soil moisture and reduce watering frequency.
- Rain Barrels: Collect rainwater for use in your garden.
- Timing: Watering in the early morning or late afternoon can minimize evaporation and improve absorption.
Pest and Disease Management in Gardening
Pest and disease issues can threaten your garden’s health. Understanding common threats and how to manage them is pivotal for sustaining growth.
Common Garden Pests and How to Identify Them
Familiarize yourself with common pests like aphids, snails, and spider mites. Look for signs such as:
- Discoloration or wilting leaves
- Webs or unusual growths on plants
- Presence of insect eggs
Natural Remedies for Pest Control
Instead of chemicals, consider organic methods for pest control:
- Neem Oil: Acts as a natural pesticide.
- Insecticidal Soap: A safer option to combat soft-bodied pests.
- Beneficial Insects: Introducing ladybugs or lacewings can help keep pest populations in check.
Preventative Measures for Disease Management
Adopt practices to prevent disease from affecting your garden:
- Rotate crops to prevent soil-borne diseases.
- Maintain proper spacing between plants to improve airflow and reduce humidity.
- Keep the garden clean by removing debris and dead plants to deter disease spread.
Harvesting and Maintenance Tips for Continued Success
Regular maintenance and harvesting are key to a successful garden. Understanding the right timing and techniques for both tasks will keep your plants healthy and productive.
When and How to Harvest Your Crops
Knowing when to harvest can significantly affect the yield and flavor of your produce. Consider these tips:
- Harvest vegetables early in the morning for optimum freshness.
- Monitor growth stages; for example, tomatoes should be firm and slightly soft to the touch, while bell peppers should reach their ideal size before picking.
- Use sharp tools to minimize damage to the plant during harvesting.
Seasonal Maintenance Routines
Establishing regular maintenance routines throughout the year can enhance garden health:
- Spring: Clean the garden beds, sharpen tools, and prepare soil for planting.
- Summer: Monitor for pests, and keep up with watering and weeding.
- Fall: Collect fallen leaves and prepare the garden for winter by mulching.
Preparing Your Garden for the Next Season
As the growing season concludes, preparing your garden for the next season is crucial:
- Clear away dead plants and debris to reduce pest and disease risks.
- Apply compost or organic fertilizers to enhance soil nutrients during winter.
- Plan crop rotations for the upcoming season to maintain soil health and fertility.