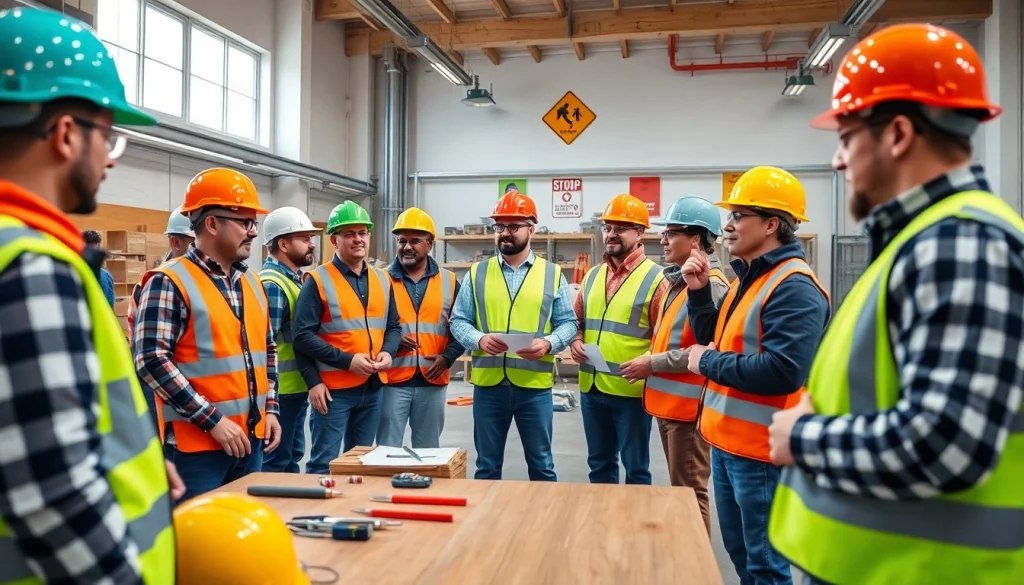
Understanding the Need for Construction Safety Training
Construction sites are inherently dangerous environments filled with various hazards that can lead to accidents and injuries. Therefore, effective construction safety training is essential in minimizing risks and ensuring the safety of all personnel involved. This article delves deep into the necessity of safety training, its key components, implementation strategies, effectiveness measurement, and answers to frequently asked questions regarding this vital subject.
Importance of Workplace Safety
Workplace safety is not just a regulatory obligation; it is a moral responsibility. The importance of workplace safety in the construction industry cannot be overstated, as it directly affects employee well-being, corporate reputation, and financial performance. Providing a safe work environment enhances employee morale and productivity while reducing costs associated with accidents and liabilities.
Moreover, companies that prioritize safety often experience lower insurance rates and reduced downtime resulting from workplace accidents. In a sector where physical labor is a daily component, fostering a culture of safety drives not only compliance but also a proactive approach to risk management.
Common Hazards in Construction
Construction sites present myriad hazards including falls, equipment-related injuries, electrical incidents, and exposure to harmful substances. Specifically, the leading causes of work-related fatalities in construction include:
- Falls: The majority of fatalities in the construction industry result from falls from heights, scaffolding, or unprotected edges.
- Being Struck By Objects: Tools, equipment, or material may fall and strike workers, causing severe injuries.
- Electrocutions: Contact with electrical wires or unsafe use of electrical equipment can lead to lethal outcomes.
- Caught-in/Between: Workers can become trapped or caught in machinery, leading to serious injuries.
Recognizing and understanding these hazards is the first step towards effective prevention through tailored training programs.
The Role of OSHA Regulations
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establishes regulatory standards that mandate construction site safety protocols. OSHA regulations are designed to protect workers from workplace hazards, setting forth guidelines on training, equipment, and safety practices. Compliance with these regulations is not only crucial for legal adherence but also fosters a culture of safety.
Employers are required to provide a safe working environment, which entails identifying potential hazards, implementing safety measures, and offering construction safety training to their workers. Understanding OSHA regulations enables construction companies to create effective strategies for on-site safety.
Key Components of Construction Safety Training
Understanding the structure and elements of construction safety training is crucial for the development of effective training programs. The components generally fall into three categories: types of training programs, essential safety equipment, and training methods and approaches.
Types of Training Programs
Various training programs cater to the unique needs of construction workers. Companies should opt for tailored training that reflects their specific risks and operational practices. Key types include:
- Induction Training: New employees receive basic safety training to understand workplace protocols and hazards.
- Specialized Training: Focused on specific tasks or equipment, such as scaffolding safety or heavy machinery operation.
- Refresher Courses: Continuation training that reinforces prior knowledge and updates workers on new regulations or equipment.
- Emergency Response Training: Teaching employees how to respond to emergencies, including evacuations and first aid.
Choosing the right combination of training types ensures that employees are well-prepared to maintain safety on site.
Essential Safety Equipment
Part of any construction safety training program must include the effective use of personal protective equipment (PPE). Properly chosen and correctly used PPE can greatly reduce the likelihood of injury. Essential safety equipment includes:
- Hard Hats: Protects workers from falling debris and head injuries.
- High-Visibility Clothing: Ensures workers are easily seen, reducing accidents.
- Safety Glasses: Shields eyes from flying debris and harmful substances.
- Hearing Protection: Reduces exposure to hazardous noise levels.
- Fall Protection Systems: Includes harnesses, guardrails, and nets.
Effective training must ensure that workers not only wear the correct PPE but also understand its purpose and proper usage.
Training Methods and Approaches
The effectiveness of training largely depends on the methods used to impart knowledge. Popular training methods include:
- On-the-Job Training: Hands-on training with real-time supervision aids skill enhancement.
- Classroom-Based Learning: Traditional method, ideal for theoretical knowledge and discussions.
- Online Training Modules: Flexible and accessible training with resources available at employees’ convenience.
- Simulation and Drills: Practical drills enhance preparedness for real-life scenarios, especially for emergencies.
Utilizing a blend of these methods can cater to different learning styles, making the training more effective.
Implementing Construction Safety Training Programs
The transition from understanding the need for construction safety training to its implementation involves several systematic steps. These include assessing training needs, creating a training schedule, and evaluating employee comprehension.
Assessing Training Needs
Before implementing safety training, it is crucial to assess the specific needs of the workforce. This involves evaluating the existing safety protocols, identifying competencies, and pinpointing knowledge gaps. Conducting surveys, interviews, and safety audits can provide valuable insights into areas that need focused training attention.
Employers should also consider factors such as the types of construction work being performed, the experience levels of workers, and past accident data in determining training needs, ensuring that training is effective and relevant.
Creating a Training Schedule
Establishing a systematic training schedule ensures that all employees receive timely exposure to important safety information. Training should be conducted regularly to keep safety awareness fresh in employees’ minds, especially when new equipment or protocols are introduced. An effective training schedule might include:
- Initial training for new hires before they begin work.
- Monthly safety meetings to review procedures and discuss incidents.
- Annual refresher courses to update knowledge and skills.
- On-demand training sessions for evolving safety challenges.
Utilizing an organized calendar can help keep everyone accountable for their ongoing education regarding safety measures.
Evaluating Employee Comprehension
Assessment of employee comprehension is essential to ensure that the training has been effective. Employers should utilize various methods to evaluate understanding, such as tests, quizzes, and practical demonstrations. Regularly measuring comprehension helps identify knowledge retention and areas needing additional focus. Moreover, implementing feedback sessions allows employees to express their concerns and suggestions regarding the training, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Safety Training
Once safety training programs have been implemented, measuring their effectiveness is crucial to ongoing success. This can be achieved through several mechanisms, including key performance indicators, soliciting feedback, and making adjustments based on outcomes.
Key Performance Indicators
Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) related to training effectiveness is essential for tracking performance over time. Typical KPIs for construction safety training include:
- Reduction in incident rates, including accidents and near misses.
- Increased safety audit scores.
- Enhanced employee satisfaction with workplace safety.
- Improved knowledge retention percentages from assessments.
Monitoring these KPIs allows management to gauge the success of training efforts and provides a foundation for strategic adjustments.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Feedback from employees regarding training sessions is invaluable for the continuous improvement of safety training programs. This can be collected through surveys, focus groups, or direct interviews. Actively soliciting employee feedback reveals underlying issues or topics that require more attention.
Moreover, fostering an environment where workers feel comfortable voicing their opinions allows for a proactive safety culture, ultimately contributing to the overall effectiveness of safety measures.
Training Adjustments Based on Outcomes
Adjusting the training program based on the feedback and performance metrics is crucial for staying current with the ever-evolving safety landscape. For instance, if certain hazards remain prevalent despite training efforts, consider refining the training material or delivery method. Regular reviews of training content and methodologies should be conducted to incorporate new insights and best practices from the industry.
By making ongoing adjustments, organizations demonstrate their commitment to safety and employee well-being, reinforcing the importance of safety training in the construction industry.
Frequently Asked Questions About Construction Safety Training
What is construction safety training?
Construction safety training equips workers with the knowledge and skills to recognize and mitigate hazards on the job site, ensuring a safer working environment.
Who should undergo safety training?
All construction personnel, including new hires, supervisors, and subcontractors, should undergo safety training to comply with regulations and ensure a safe workplace.
How often should safety training be conducted?
Safety training should occur at least annually, with ongoing refreshers as needed and additional training when new equipment or procedures are introduced.
What topics should be covered?
Training should cover hazard recognition, proper equipment use, emergency procedures, PPE, and OSHA regulations, focusing on the specific risks of the site.
Are there certifications for completeness?
Yes, many organizations offer certifications for safety training programs, ensuring that training meets industry standards and regulatory requirements.